Product Description
48V 1kw brushless dc servo motor with encoder for AGV robot
Product Features
Protection grade:IP65, insulation grade:F
Winding overhang structure optimization, to minimize the copper loss and iron loss minimization, small volume, light weight, low temperature rise, high efficiency
Super high coercivity, the maximum magnetic energy product NdFe35 permanent magnetic materials, strong resistance to demagnetization, motor performance is stable.
Low noise, low vibration, low moment of inertia.
High torque, fast dynamic response, wide speed range, strong overload capacity (four times)
Features:
*High Torque to inertia ratio&up to 25000Nm/kgm²
*Fast dynamic response *time constant <20ms
*Wide speed adjusting&feedback up to 1000:1
*Steady speed precision up to 0.5%
*High overload,2Mn/30s,3.5N.m/10s
*Small volume and light
*Silent,the lowest noise is only 45dB(A)
*Protected with IP65,Class F insulation
Industry class
1.The altitude should be over 1000 CHINAMFG above sea level
2.Environment temperature:+5ºC~+40ºC
3.The month average tallest relative humidity is 90%,at the same the month average lowest temperature is less than 25
| Model | KY110AS0408-15 |
| VOLT | 48VDC |
| POWER | 800W |
| SPEED | 1500RPM |
| TORQUE | 6.3N.M |
| ENCODER | 2500PPR |
| Application: | Industrial |
|---|---|
| Operating Speed: | Adjust Speed |
| Excitation Mode: | Excited |
| Function: | Control, Driving |
| Casing Protection: | Protection Type |
| Number of Poles: | 10 |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
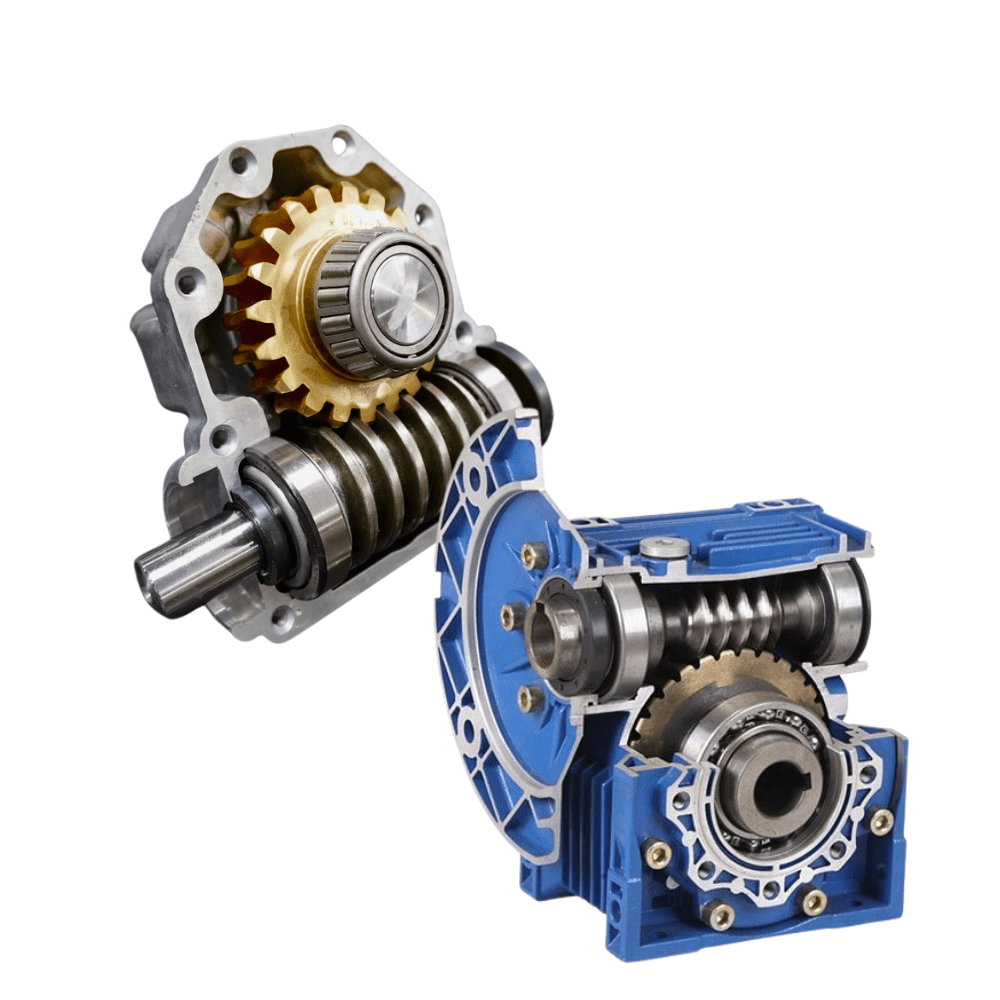
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using a worm gear?
A worm gear offers several advantages and disadvantages that should be considered when selecting it for a specific application. Here’s a detailed explanation of the advantages and disadvantages of using a worm gear:
Advantages of using a worm gear:
- High gear reduction ratio: Worm gears are known for their high gear reduction ratios, which allow for significant speed reduction and torque multiplication. This makes them suitable for applications that require precise motion control and high torque output.
- Compact design: Worm gears have a compact design, making them space-efficient and suitable for applications where size is a constraint. The worm gear’s compactness allows for easy integration into machinery and equipment with limited space.
- Self-locking capability: One of the key advantages of a worm gear is its self-locking property. The angle of the worm thread prevents the reverse rotation of the output shaft, eliminating the need for additional braking mechanisms. This self-locking feature is beneficial for maintaining position and preventing backdriving in applications where holding the load in place is important.
- Quiet operation: Worm gears typically operate with reduced noise levels compared to other gear types. The sliding action between the worm and the worm wheel teeth results in smoother and quieter operation, making them suitable for applications where noise reduction is desired.
- High shock-load resistance: Worm gears have good shock-load resistance due to the sliding contact between the worm and the worm wheel teeth. This makes them suitable for applications that involve sudden or intermittent loads, such as lifting and hoisting equipment.
- Easy installation and maintenance: Worm gears are relatively easy to install and maintain. They often come as a compact unit, requiring minimal assembly. Lubrication maintenance is crucial for optimal performance and longevity, but it is typically straightforward and accessible.
Disadvantages of using a worm gear:
- Lower efficiency: Worm gears tend to have lower mechanical efficiency compared to some other gear types. The sliding action between the worm and the worm wheel teeth generates higher frictional losses, resulting in reduced efficiency. However, efficiency can be improved through careful design, quality manufacturing, and proper lubrication.
- Limited speed capability: Worm gears are not suitable for high-speed applications due to their sliding contact and the potential for heat generation. High speeds can lead to increased friction, wear, and reduced efficiency. However, they excel in low to moderate speed applications where high torque output is required.
- Heat generation: The sliding action between the worm and the worm wheel generates friction, which can result in heat generation. In high-load or continuous-duty applications, this heat buildup can affect the efficiency and longevity of the system. Proper lubrication and heat dissipation measures are necessary to mitigate this issue.
- Less suitable for bidirectional motion: While worm gears offer excellent self-locking capabilities in one direction, they are less efficient and less suitable for bidirectional motion. Reversing the direction of the input or output shaft can lead to increased friction, reduced efficiency, and potential damage to the gear system.
- Lower accuracy in positioning: Worm gears may have lower accuracy in positioning compared to some other gear types, such as precision gear systems. The sliding contact and inherent backlash in worm gears can introduce some degree of positioning error. However, for many applications, the accuracy provided by worm gears is sufficient.
- Potential for wear and backlash: Over time, the sliding action in worm gears can lead to wear and the development of backlash, which is the play or clearance between the worm and the worm wheel teeth. Regular inspection, maintenance, and proper lubrication are necessary to minimize wear and reduce backlash.
When considering the use of a worm gear, it’s essential to evaluate the specific requirements of the application and weigh the advantages against the disadvantages. Factors such as torque requirements, speed limitations, positional stability, space constraints, and overall system efficiency should be taken into account to determine if a worm gear is the right choice.

Can worm gears be used in both horizontal and vertical orientations?
Yes, worm gears can be used in both horizontal and vertical orientations. Here’s a detailed explanation of the suitability of worm gears for different orientations:
1. Horizontal Orientation: Worm gears are commonly used in horizontal orientations and are well-suited for such applications. In a horizontal configuration, the worm gear’s weight is primarily supported by the bearings and housing. The lubrication and load-carrying capabilities of the gear design are optimized for horizontal operation, allowing for efficient power transmission and torque generation. Horizontal worm gear applications include conveyor systems, mixers, mills, and many other industrial machinery setups.
2. Vertical Orientation: Worm gears can also be used in vertical orientations, although there are some additional considerations to address in such cases. In a vertical configuration, the weight of the worm gear exerts an axial force on the worm shaft, which can introduce additional load and affect the gear’s performance. To ensure proper operation in a vertical orientation, the following factors should be considered:
- Thrust load handling: Vertical orientations impose a thrust load on the worm gear due to the weight of the gear and any additional external loads. The gear design should be capable of handling and transmitting this thrust load without excessive wear or deformation. Proper bearing selection and lubrication are crucial to support the axial load and maintain optimal performance.
- Lubrication: Lubrication becomes even more critical in vertical worm gear applications. Adequate lubrication ensures proper lubricant film formation to minimize friction, reduce wear, and dissipate heat generated during operation. Careful consideration should be given to the lubricant type, viscosity, and lubrication method to ensure effective lubrication, particularly in the upper parts of the gear where lubricant distribution may be more challenging.
- Backlash control: In vertical orientations, gravity can cause the load to act on the gear in the opposite direction, potentially leading to increased backlash. Proper gear design, including tooth geometry and clearance adjustments, can help minimize backlash and ensure precise motion control and positional stability.
- Bearing selection: The choice of bearings becomes crucial in vertical worm gear applications. Thrust bearings or combinations of thrust and radial bearings may be required to handle the axial and radial loads effectively. Bearings with appropriate load-carrying capacities and stiffness are selected to ensure smooth operation and minimize deflection under vertical loads.
- Sealing: Vertical orientations may require additional sealing measures to prevent lubricant leakage and ingress of contaminants. Proper sealing and protection mechanisms, such as seals or gaskets, should be implemented to maintain the integrity of the gear system and ensure reliable operation.
In summary, worm gears can be utilized in both horizontal and vertical orientations. However, certain considerations related to thrust load handling, lubrication, backlash control, bearing selection, and sealing should be taken into account for vertical applications. By addressing these factors appropriately, worm gears can effectively transmit power and torque, whether in horizontal or vertical configurations.

How do you install a worm gear system?
Installing a worm gear system requires careful attention to ensure proper alignment, lubrication, and secure mounting. Here are the general steps involved in installing a worm gear system:
- Prepare the components: Before installation, ensure that all the components of the worm gear system, including the worm, worm wheel, bearings, and housing, are clean and free from any contaminants or damage. Inspect the components for any signs of wear or defects.
- Check alignment: Verify that the mating surfaces of the worm and worm wheel are clean and free from any debris. Ensure that the gear teeth mesh properly and that there is no excessive backlash or misalignment. Make any necessary adjustments or repairs before proceeding with the installation.
- Apply lubrication: Lubricate the worm gear system according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Select a suitable lubricant that provides sufficient lubrication and reduces friction between the worm and worm wheel during operation. Apply the lubricant evenly to the gear teeth and other contact surfaces.
- Mounting: Position the worm gear system in the desired location, taking into account any space constraints or mounting requirements. Use appropriate fasteners, such as bolts or screws, to securely attach the system to the surrounding structure or base. Ensure that the mounting surfaces are clean, flat, and able to withstand the forces and loads exerted by the gear system.
- Alignment and adjustment: Once the worm gear system is mounted, check the alignment again and make any necessary adjustments. Ensure that the worm and worm wheel are properly engaged and that there is no excessive play or binding. Pay attention to any specified alignment tolerances provided by the manufacturer.
- Testing and operation: After installation, conduct a thorough functional test of the worm gear system. Verify that it operates smoothly, without unusual noise or vibration. Check for proper engagement of the gear teeth and ensure that the system performs as intended under different load conditions. Monitor the system’s performance during initial operation and address any issues or abnormalities promptly.
It’s important to follow the specific installation instructions provided by the gear system manufacturer. Different worm gear designs and applications may have additional installation requirements or considerations that should be taken into account.
Proper installation of a worm gear system ensures its reliable operation, minimizes wear, and maximizes its lifespan. If you are unsure about any aspect of the installation process, it is recommended to consult the manufacturer or seek the assistance of a qualified professional.


editor by CX 2023-09-22